Published on 2025-06-29T20:33:01Z
What is Accessibility? Key Concepts & Best Practices
Accessibility refers to the practice of designing websites that can be used by people with a wide range of abilities and disabilities.
By following accessibility guidelines such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), designers ensure that visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments do not hinder the user experience.
Accessible websites not only comply with legal standards like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) but also benefit from improved SEO, enhanced user engagement, and higher conversion rates.
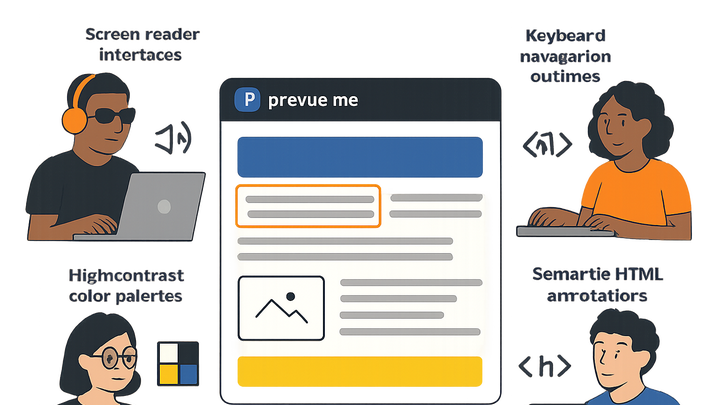
Incorporating accessibility best practices, such as semantic HTML, sufficient color contrast, meaningful alt text, and keyboard-friendly navigation, broadens your audience and fosters inclusivity.
Tools like Prevue.me can audit your site for accessibility issues and provide actionable recommendations to boost both user satisfaction and lead generation.
Accessibility
Accessible website design ensures all users can interact effectively, boosting UX, SEO, and CRO with WCAG-aligned best practices.
Why Accessibility Matters
Ensuring web accessibility isn’t just about compliance; it’s about creating an inclusive experience that benefits every user. Accessible sites reduce legal risks, improve usability for people with disabilities, and deliver SEO and conversion rate optimization (CRO) advantages. By prioritizing accessibility, businesses can reach a wider audience and foster brand loyalty.
-
Legal compliance
Websites must adhere to regional laws to avoid lawsuits and penalties.
- Ada (americans with disabilities act):
In the U.S., many businesses are required to make websites accessible under ADA standards.
- Section 508:
Federal requirement for U.S. government agencies to ensure digital accessibility.
- Ada (americans with disabilities act):
-
Enhanced user experience
Designing for accessibility leads to a smoother experience for all users.
- Inclusive design:
Consideration of diverse abilities results in clearer layouts and interactions.
- Inclusive design:
-
Seo & cro benefits
Accessible elements often align with SEO best practices and remove friction for conversions.
- Better crawlability:
Semantic HTML helps search engines index content more effectively.
- Higher conversion rates:
Clear structure and navigation reduce barriers, boosting form submissions and sales.
- Better crawlability:
Key Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG 2.1)
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 provide a framework around four core principles: perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust. Each principle includes success criteria to ensure content is accessible to users with various disabilities.
-
Perceivable
Information and UI components must be presented in ways users can perceive, such as providing text alternatives.
- Alt text:
Supply descriptive alt attributes for images and non-text content to aid screen readers.
- Alt text:
-
Operable
User interface components must be operable via keyboard and must not cause seizures.
- Keyboard navigation:
Ensure all interactive elements are reachable and usable through a keyboard.
- Keyboard navigation:
-
Understandable
Content should be readable and predictable to users.
- Clear language:
Use plain language and avoid complex jargon.
- Clear language:
-
Robust
Content must be compatible with various user agents, including assistive technologies.
- Aria roles:
Use ARIA attributes to enhance the semantic meaning of dynamic content.
- Aria roles:
Implementing Accessibility in Web Critiques
When auditing a website for CRO, UX, and SEO, integrating accessibility checks ensures a holistic evaluation and uncovers issues that affect all users. Accessibility best practices often overlap with SEO and conversion optimization techniques.
-
Semantic html
Use correct HTML elements to convey meaning naturally and improve assistive technology support.
- Heading structure:
Organize content with h1–h6 tags to create a logical outline.
- Button elements:
Prefer
<button>over clickable<div>to ensure native keyboard support and accessibility.<button>Submit</button>
- Heading structure:
-
Color contrast & visuals
Ensure text and interface elements meet minimum contrast ratios for readability.
- Contrast ratio:
Maintain at least 4.5:1 contrast for normal text and 3:1 for large text.
- Contrast ratio:
-
Media accessibility
Make audio and video content accessible to users with hearing or visual impairments.
- Captions & transcripts:
Provide synchronized captions for video and transcripts for audio-only content.
- Captions & transcripts:
Testing and Tools
Numerous tools automate accessibility testing and provide actionable insights. Integrating these into your audit workflows helps track improvements and maintain compliance.
-
Prevue.me
A SaaS platform for automated site critiques covering CRO, UX, SEO, and accessibility with prioritized recommendations.
- Actionable reports:
AI-driven reports highlight issues by severity and offer specific fixes to enhance lead generation.
- Continuous monitoring:
Receive alerts on regressions and track improvements over time.
- Actionable reports:
-
Wave
A free Chrome extension that visualizes accessibility errors directly on the page.
- Visual indicators:
Icons and outlines show error locations and type with suggestions.
- Visual indicators:
-
Lighthouse
Google’s integrated tool in Chrome DevTools for auditing performance, accessibility, SEO, and best practices.
- Accessibility score:
Provides a score with detailed diagnostics and improvement opportunities.
- Accessibility score: