Published on 2025-06-29T22:02:12Z
What is Information Architecture? Examples and Best Practices for CRO, UX, and SEO
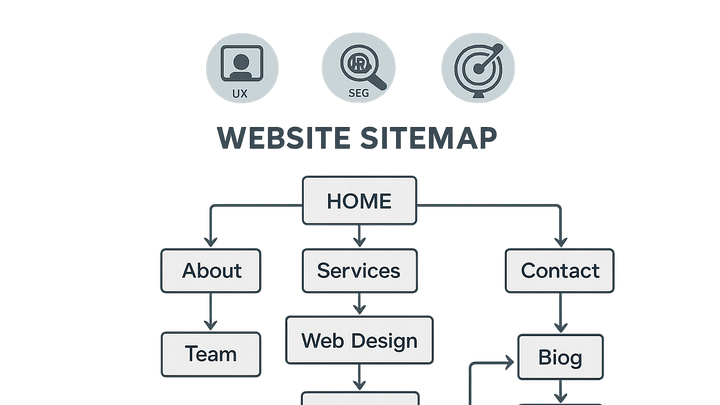
Information Architecture (IA) is the practice of organizing, structuring, and labeling content within a website or application to support usability and findability. In CRO (Conversion Rate Optimization), IA guides users through clear pathways that lead to desired actions, reducing friction and improving conversion rates. From a UX perspective, a well-defined IA reduces cognitive load, simplifies navigation, and enhances overall satisfaction. In SEO, IA influences crawlability and indexing by search engines, ensuring content is discoverable and ranked appropriately. Tools like Prevue.me can analyze your site’s IA, offering actionable critiques on navigation structure, internal linking, and content organization to boost lead generation, accessibility, and search visibility. A robust IA also provides a scalable framework that adapts as your content grows, maintaining consistency and helping teams manage updates efficiently.
Information architecture
Organizing and labeling website content to enhance findability, UX, SEO, and conversion optimization.
Why Information Architecture Matters for CRO, UX, and SEO
Information Architecture is central to guiding users, improving engagement, and optimizing for search engines and conversions.
-
Findability and navigation
Effective IA ensures users locate content quickly through clear menus, logical hierarchies, and intuitive labels.
- Hierarchical menus:
Organize content into parent and child categories to reflect user mental models.
- Labels and terminology:
Use consistent, user-centric language that matches search queries and expectations.
- Search functionality:
Implement predictive search and filters to help users refine results.
- Hierarchical menus:
-
Conversion pathways
A structured IA guides users along optimized journeys toward key conversion points, such as sign-up forms or product pages.
- Clear call-to-actions:
Position CTAs within the logical flow of content to reduce friction.
- Linear vs. flexible paths:
Balance straightforward funnels with alternative navigation for exploration.
- Progress indicators:
Show users where they are in multi-step processes to reduce drop-offs.
- Clear call-to-actions:
-
Seo and crawlability
Search engines depend on IA to index pages correctly; a logical structure improves ranking potential.
- Url structures:
Reflect site hierarchy in URLs to convey topic relevance.
- Internal linking:
Link related content to distribute link equity and improve navigation.
- Metadata organization:
Standardize title tags and meta descriptions in alignment with IA.
- Url structures:
-
Accessibility and usability
Proper IA underpins accessibility by ensuring content is logically ordered for assistive technologies.
- Heading hierarchy:
Use h1-h6 tags in a sequential order to create a clear content outline.
- Aria landmarks:
Implement landmarks to help screen reader users navigate sections.
- Consistent layouts:
Maintain predictable page structures across the site.
- Heading hierarchy:
Core Principles of Information Architecture
Adhering to foundational IA principles ensures content is organized in a scalable and user-centric manner.
-
Organization systems
Define how content is grouped to match user expectations and business needs.
- Hierarchical:
Tree-like structures that flow from general to specific topics.
- Faceted:
Allow multiple classification schemes for dynamic filtering.
- Hierarchical:
-
Labeling systems
Develop consistent naming conventions that improve usability and search accuracy.
- Standardized terminology:
Use industry and user language in labels.
- Avoid jargon:
Simplify complex terms to enhance comprehension.
- Standardized terminology:
-
Navigation systems
Design menus, links, and pathways that support primary user journeys.
- Global navigation:
Persistent menus that provide access to main site sections.
- Local navigation:
Secondary menus for subsections within a page.
- Breadcrumbs:
Sequential links that show the current page’s location within the hierarchy.
- Global navigation:
-
Search systems
Implement search interfaces to complement browsing by offering direct access to content.
- Auto-suggest:
Display predicted queries as users type.
- Filterable results:
Enable facets to refine search output.
- Auto-suggest:
Methods to Evaluate and Improve IA
Use qualitative and quantitative techniques to identify IA strengths and weaknesses, then iterate for improvement.
-
Card sorting
Engage users in grouping topics to reveal their mental models.
- Open card sorting:
Participants create their own category names.
- Closed card sorting:
Participants sort cards into predefined categories.
- Open card sorting:
-
Tree testing
Test how easily users find items in a simplified site structure without UI distractions.
- Task completion rates:
Measure success in locating information.
- Path analysis:
Track the navigation paths taken.
- Task completion rates:
-
Analytics review
Leverage tools like Google Analytics to discover navigation drop-offs and popular search terms.
- Behavior flow:
Visualize common user journeys and exit points.
- Site search reports:
Identify what users look for and refine labels accordingly.
- Behavior flow:
-
Usability testing
Observe real users interacting with the IA to gather qualitative feedback.
- Think-aloud protocol:
Ask users to verbalize thoughts as they navigate.
- Success metrics:
Record time to complete tasks and satisfaction scores.
- Think-aloud protocol:
Auditing IA with Prevue.me
prevue.me offers automated and expert-driven critiques to assess and enhance your site’s IA for better CRO, UX, SEO, and accessibility.
-
Structure analysis
Evaluate your site’s hierarchy and navigation depth to spot overly complex or shallow structures.
- Depth metrics:
Analyze the number of clicks from the homepage to key pages.
- Orphan pages detection:
Identify pages without inbound links in the main structure.
- Depth metrics:
-
Navigation clarity report
Review consistency and clarity of menu labels and link placements.
- Label effectiveness:
Assess whether labels match user search language and expectations.
- Menu consistency:
Check for uniform menu structures across pages.
- Label effectiveness:
-
Internal linking insights
Optimize link placement to distribute authority and guide users through content.
- Link depth:
Ensure critical pages receive prominent links from multiple locations.
- Anchor text quality:
Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchors.
- Link depth:
-
Seo and accessibility recommendations
Generate prioritized actions to improve metadata, heading structures, and ARIA landmarks.
- Meta tag audit:
Identify missing or duplicate title tags and meta descriptions.
- Heading hierarchy review:
Verify sequential heading order and proper usage.
- Meta tag audit:
Best Practices for Ongoing IA Maintenance
Maintaining IA is crucial as content evolves to preserve usability and SEO performance.
-
Ia governance
Define roles, responsibilities, and workflows for IA decisions.
- Ownership matrix:
Assign clear accountability for IA elements.
- Review cycles:
Set regular intervals for IA audits.
- Ownership matrix:
-
Content inventory and audits
Keep a detailed catalog of all pages and assets to manage updates and retirements.
- Inventory tools:
Use spreadsheets or specialized software to track content.
- Gap analysis:
Identify missing content and redundancies.
- Inventory tools:
-
Documentation and style guides
Publish IA guidelines to ensure consistency across teams.
- Taxonomy guidelines:
Standardize category and tag usage.
- Labeling conventions:
Document naming rules for menus and links.
- Taxonomy guidelines:
-
Continuous user feedback
Solicit ongoing feedback to adapt IA to changing user needs.
- Surveys and feedback widgets:
Integrate feedback tools directly on key pages.
- Periodic testing:
Run mini card sorts or tree tests after major updates.
- Surveys and feedback widgets: