Published on 2025-06-29T19:30:27Z
What is a Sitemap? Examples of Effective Sitemaps
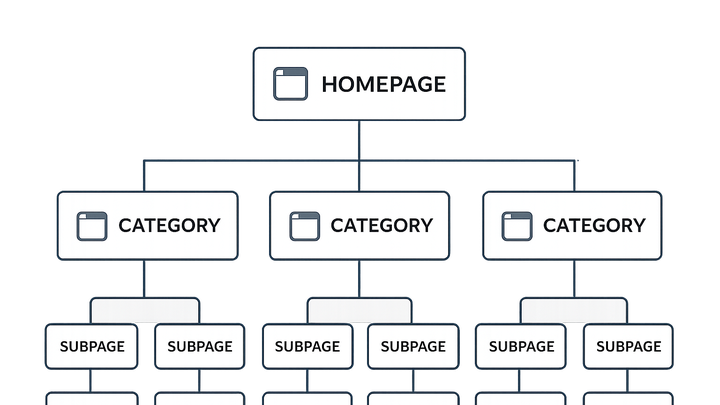
A sitemap is a file or page that lists all URLs of a website in a hierarchical structure. It helps search engines discover and index content efficiently, and offers visitors an overview of available pages. There are two main types: XML sitemaps designed for crawlers, and HTML sitemaps tailored for human navigation. By improving crawlability, navigation, and visibility of key pages, sitemaps support SEO, UX, and conversion rate optimization (CRO) efforts. Tools like Prevue.me can audit your sitemap to uncover missing pages, errors, and optimization opportunities across SEO, UX, accessibility, and CRO. Maintaining an accurate, well-structured sitemap is essential for guiding both users and search engines toward your most valuable content.
Sitemap
A sitemap lists website URLs for search engines and users, boosting crawlability, navigation, SEO, and conversion optimization.
Definition and Purpose
A sitemap serves as a roadmap for a website, listing all pages to both search engines and users. It ensures important content is discovered, enhances crawlability, and improves user navigation while supporting conversion goals.
-
Core functions of sitemaps
Sitemaps enable comprehensive indexing by search engines, offer users an overview of site structure, and highlight key conversion pages to guide visitors toward desired actions.
- Search engine guidance:
Provides crawlers like Googlebot with a clear list of URLs, ensuring timely discovery and indexing of content.
- User navigation aid:
HTML sitemaps present a navigable page structure, helping visitors locate content quickly and reducing bounce rates.
- Conversion optimization:
Emphasizes critical landing pages and CTAs, directing users toward high-value actions and boosting lead generation.
- Search engine guidance:
Types of Sitemaps
Websites commonly use XML sitemaps for search engines and HTML sitemaps for human visitors. Each type has unique tags, formats, and purposes.
-
Xml sitemaps
An XML file that lists URLs with metadata tags to inform search engine crawlers about page priority and update frequency.
- Url entries:
Includes <loc>, <lastmod>, <changefreq>, and <priority> tags to guide crawler behavior.
- Metadata tags:
Signals how often content changes and which pages are most important for indexing.
- Search console submission:
Can be submitted via Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools to accelerate indexing.
- Url entries:
-
Html sitemaps
A human-readable page listing all site links hierarchically, improving site navigation and accessibility.
- Link structure:
Organized by section or topic to help users browse logically through content.
- Accessibility:
Ensures assistive technologies can parse site structure, enhancing usability for all visitors.
- Link structure:
Benefits for SEO, UX, and CRO
Sitemaps offer cross-disciplinary advantages: they improve search engine visibility, enhance user experience, and support conversion rate optimization by guiding visitors toward key pages.
-
Seo advantages
By listing all relevant URLs, sitemaps improve crawl coverage, reveal indexing issues, and hint at page importance.
- Crawl efficiency:
Reduces reliance on internal links alone, ensuring even deep pages are discovered by crawlers.
- Error detection:
Search Console reports highlight broken links or blocked pages within the sitemap for quick fixes.
- Priority signaling:
Priority tags can underscore critical pages, though actual crawler behavior may vary.
- Crawl efficiency:
-
Ux improvements
HTML sitemaps help users find content faster, lower frustration, and reduce bounce rates.
- User orientation:
Gives visitors a bird’s-eye view of your site, making it easier to navigate.
- Content discoverability:
Surfaces deep or less-trafficked pages to increase engagement.
- User orientation:
-
Cro impact
Well-structured sitemaps guide users directly to conversion points, enhancing lead generation and form submissions.
- Goal pathways:
Maps out clear routes to CTAs and landing pages for smoother user journeys.
- Lead generation:
Highlights key forms and product pages, supporting prevue.me’s actionable critiques to maximize conversions.
- Bounce rate reduction:
Intuitive site maps keep visitors engaged longer by reducing dead-ends.
- Goal pathways:
Best Practices for Creating and Maintaining Sitemaps
Adhere to these guidelines to ensure your sitemaps remain accurate, efficient, and aligned with SEO and UX standards.
-
Regular updates
Automate sitemap regeneration after adding, removing, or updating pages to keep it current.
-
Size management
Limit each XML sitemap to 50,000 URLs and 50MB; use a sitemap index file for larger sites.
-
Validation and testing
Use XML validators and Search Console reports to detect syntax errors and unreachable URLs.
-
Submission and monitoring
Submit sitemaps to search consoles and regularly review coverage reports to resolve issues promptly.
Auditing Your Sitemap with Prevue.me
prevue.me offers end-to-end audits of your sitemap’s SEO, UX, accessibility, and CRO performance, delivering prioritized, actionable insights.
-
Seo & crawlability audits
prevue.me identifies missing pages, broken links, and priority tag discrepancies to enhance indexing.
- Missing urls:
Detects pages on your site that aren’t included in the sitemap for comprehensive coverage.
- Broken links:
Flags 404 or redirected URLs in your sitemap to eliminate crawler errors.
- Priority & frequency issues:
Highlights URLs with misconfigured <priority> and <changefreq> tags for adjustment.
- Missing urls:
-
Ux & accessibility insights
Analyzes HTML sitemap clarity, link visibility, and ARIA compliance to improve user navigation.
- Screen reader compatibility:
Checks for ARIA roles and semantic markup to ensure assistive technologies interpret your sitemap correctly.
- Link visibility:
Assesses font size, contrast, and spacing to ensure links are easily identifiable.
- Hierarchy clarity:
Evaluates logical nesting and labeling of categories for intuitive browsing.
- Screen reader compatibility: