Published on 2025-06-29T19:37:53Z
What is a User Flow? Examples for Website CRO/UX/SEO
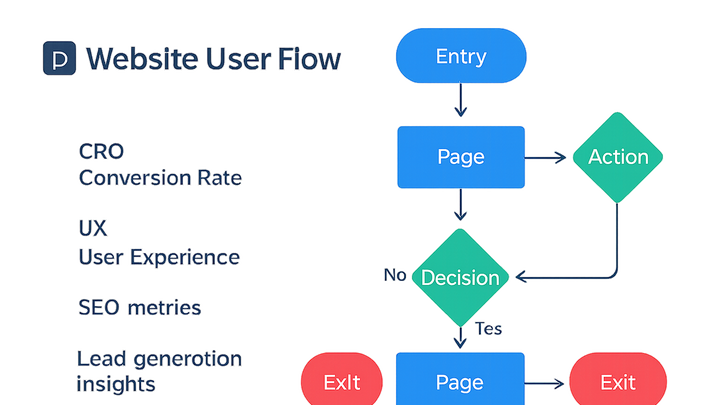
A user flow is a visual map of the series of actions a visitor takes on a website to complete a task, such as signing up for a newsletter or making a purchase. It outlines entry points, actions, decision nodes, and exit points. In the context of website criticism for CRO, UX, and SEO, user flows help identify friction points and optimize each step for maximum lead generation and user satisfaction.
User flows are essential because they:
- Clarify user goals and pain points
- Highlight drop-off areas impacting conversion rates
- Inform design and content decisions for better UX
- Improve site structure for SEO crawl efficiency
Tools like Prevue.me can audit your user flows by providing actionable critiques on UX bottlenecks, SEO gaps, and accessibility issues, guiding you toward data-driven improvements.
User flow
Visual map of users' step-by-step paths on a website, guiding optimization for conversion, UX, SEO, and lead generation.
Understanding User Flow
This section introduces the core concept of user flows and their critical role in mapping visitor interactions on a website.
-
Definition
A user flow is a step-by-step visual representation of how visitors navigate through a website to accomplish a specific goal.
-
Components of a user flow
Key building blocks include entry points, actions, decision nodes, and exit points that together outline the user’s journey.
- Entry points:
Starting locations where users enter the flow, such as landing pages, ads, or search results.
- Actions:
Individual steps or interactions users take, like clicking links, filling forms, or adding items to a cart.
- Decision points:
Moments where users choose between alternatives, for example selecting a product variant or opting into a newsletter.
- Exit points:
End locations where users leave the flow, such as a confirmation page, thank-you screen, or abandonment point.
- Entry points:
Importance in CRO, UX & SEO
Explores how optimized user flows impact conversion rates, user experience, and search engine performance.
-
Conversion rate optimization
Streamlined user flows reduce friction, guiding visitors smoothly toward conversion events like form submissions or purchases.
-
User experience (ux)
Well-structured flows enhance navigation clarity, reduce bounce rates, and increase user satisfaction.
-
Search engine optimization (seo)
Logical and hierarchical flows help search engines crawl and index pages more effectively, boosting visibility and rankings.
Creating Effective User Flows
Practical steps to design, map, and refine user flows based on research, mapping tools, and iterative testing.
-
Research & data gathering
Leverage analytics platforms (e.g., Google Analytics, prevue.me) to identify common paths, drop-off points, and user behavior patterns.
-
Flow mapping techniques
Use diagram tools like Miro or Figma to visually map each step, ensuring clarity and stakeholder alignment.
-
Iterative testing & validation
Continuously refine user flows through A/B testing, session recordings, and prevue.me critiques to validate improvements.
Optimizing with Prevue.me
Using prevue.me to analyze and enhance user flows for maximum lead generation, improved UX, SEO, and accessibility.
-
Actionable critiques
prevue.me pinpoints UX bottlenecks, SEO gaps, and accessibility issues within your user flow, offering prioritized recommendations.
-
Lead generation enhancements
Identify and optimize form workflows, reduce form abandonment, and improve call-to-action placement for higher lead gen.
-
Accessibility insights
Address accessibility barriers in your flow with prevue.me’s audits to ensure inclusive design and compliance.
Best Practices & Common Pitfalls
Guidelines and warnings to ensure your user flows are both effective and user-friendly.
-
Keep it simple
Limit the number of steps and decision points to minimize cognitive load and potential drop-offs.
-
Avoid unnecessary complexity
Overly complex branches can confuse users; focus on primary conversion paths that deliver value.
-
Failing to update flows
Regularly revisit and update flows to adapt to changing user needs, content updates, and new business goals.